KonnectOpen Configuration
Overview
The KonnectOpen Configuration dialog box provides a centralized interface to manage network settings, WAN/LAN/Wi-Fi interfaces, system updates, and device transfers. This unified view simplifies editing, adding, and monitoring interfaces and configurations for each network device in your system. It enables network administrators and operators to configure devices remotely with full visibility and control.
Click the
icon from the Operations column to open the Configurations pop-up box of the selected device.
-20250730-194535%20(1)-20250811-125209.png?inst-v=a84c6a6d-1a04-4602-8458-1957efbf2cd0)
Topology
The Configurations dialog box contains the following options in its left menu bar - Interfaces, WAN, LAN, Wi-Fi, System and Association. These options can be used to create, copy and modify various configurations for the selected device.
Interfaces
The Interfaces option is selected by default. The system displays details of all pre-configured interfaces to the user. The user can view and manage all physical and virtual interfaces.
-20250811-142035.png?inst-v=a84c6a6d-1a04-4602-8458-1957efbf2cd0)
Configuration
The user can view and update the configuration of the Interfaces present on the System.
There is a flexibility that any ethernet interface on the System (applicable for all products) can be configured as either WAN interface, LAN interface or for VSAT management. Along with this flexibility, VLANs can be configured on the interfaces and the same can be configured as WAN sub-interface or as LAN access port.
Interfaces are physically labelled on the hardware device as WAN or LAN, but can be configured as either a WAN or LAN port depending on the needed function.
The user can press on the Refresh button to refresh the page and get the latest data. By default, this screen refreshes every 30 seconds.
There are three types of Interfaces i.e., WAN, LAN and WiFi.
The Interfaces table shows the following information:
Enable/Disable Toggle - Click the Enable/Disable Toggle button to enable or disable this network interface.
Name - This shows the Alias of the network interface that is available on the device.
The connection status is denoted by following convention:
Green - Connected (link up)
Red - Disconnected (link down).
Physical Interface - Shows the actual hardware port or wireless interface on the device.
Type – The logical role of the interface, such as LAN, WAN, or Wi-Fi LAN.
Link Type – Defines the operational mode of the interface link, such as LAN Trunk (carrying multiple VLANs) or Ethernet (single network link).
Assignment – Lists the networks or profiles currently mapped to that interface.
Actions - Click the
 icon to edit the Alias, Interface Type, Interface Name, Type and Network Assignments.
icon to edit the Alias, Interface Type, Interface Name, Type and Network Assignments.Use the filter buttons
 to filter the list by interface type (All, LAN, WAN, Wi-Fi).
to filter the list by interface type (All, LAN, WAN, Wi-Fi).Click the
icon to delete a Interface. Please note that only custom-created interfaces can be deleted. System-default interfaces cannot be deleted.
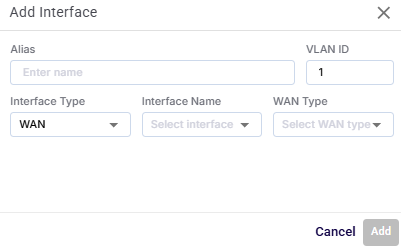
Add Interface
Click the Add Interface button to add new WAN or Wi-Fi interfaces and assign configuration details. LAN interfaces are system default and cannot be newly created.
Add Interface
In the Alias field, enter a name for the interface.
In the VLAN ID field, enter the VLAN tag associated with the interface (numeric).
In the Interface Type field, select between WAN, or Wi-Fi.
In the Interface Name field, select from the list of available physical or logical ports.
If 'WAN' is selected as Interface Type, user can also configure the WAN Type, which is one of:
Cell
Ethernet
L-Band
OneWeb
Starlink
Starlink Residential
VSAT
VSAT-HighSpeed
VSAT-Ka
VSAT-Ku
VSAT-Unlimited
VSAT-VOIP
If Interface Type is ‘LAN’, user can also configure the LAN Type, which is one of:
LAN Trunk
LAN Access.
If the interface type is set to Wi-Fi, the below additional Wi-Fi specific configuration options are shown.
Enter the SSID.
Enter the Alias.
Interface Type is selected as WIFI.
Select the Mode - WAN WI-FI or Access Point.
Select the WI-FI Band - WIFI 2.4 or WIFI 5.
Select the Security - WPA2/WPA3 or Open.
If the Security is selected as WPA2/WPA3, set a password in the Password field.
Validation occurs for duplicate alias names or reserved VLAN IDs.
The 'Add' button becomes active once all mandatory fields are filled.
Click the Add button to create the interface.
Click the Cancel button to discard the input and close the dialog.
WAN
Select the WAN option from the side menu bar to open the WAN tab. This tab enables the user to create and manage WAN Profiles with link bonding and priority.
-20250811-152355.png?inst-v=a84c6a6d-1a04-4602-8458-1957efbf2cd0)
WAN
While the KonnectOpen System is installed on the site, a default WAN Profile is created with the priority of the enabled WANs configured in this WAN Profile and assigned to the default Access Network. However, user can create multiple WAN profiles of their choice.
It is possible to configure any individual VLAN, subnet or even device in a way that the Internet traffic that entity is carried by more than one WAN link, based on conditions. This feature is called bonding, and the set of WAN links is called the ‘bonded set’. Within WAN profiles, if any priority levels contain more than one WAN link, then those links in that priority level form a bonded set. It should be noted that, should any one link in a bonded set fail, while new TCP or UDP sessions would be assigned to one of the surviving links of the bonded set, any sessions currently using that failed link will be lost.
The user can press on the Refresh button to refresh the page and get the latest data. By default, this screen refreshes every 30 seconds.
Initially, the Default WAN profile is available. User can create multiple profiles. Once, the profiles are configured, the profiles become available under the WAN Profiles section.
Switch between existing profiles by clicking the name of the WAN Profile from the left menu bar.
Click the + button to create a new WAN Profile.
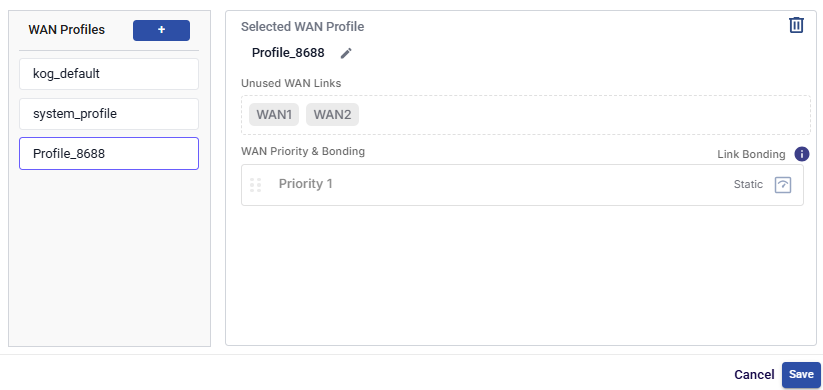
New WAN Profile
Click the
 button to edit the name of the WAN Profile.
button to edit the name of the WAN Profile.Disabled WAN sources are displayed under the section Unused WAN Links.
Note: Only Interfaces enabled on the Interfaces tab will be visible on the WAN Profile screen.
Drag and drop the WANs available from the Unused WAN Links section to the respective priority section. More than one WAN (similar or dissimilar type) can be associated with a single priority. In this case, these WANs will be bonded.
Link Bonding can be set to Static or Dynamic. By default, the link bonding type is Dynamic, in which case the system distributes the traffic on each WAN link based on performance. In Static Setting, a configured % of traffic is set for each WAN link. For details of the types of link bonding, point to i icon next to the Link Bonding. The user can configure the weighting % of the WAN link.
To configure the weighting %, perform the following steps.
Click Static button under the link bonding section.
The Weighting % section becomes available.
Enter the weighting % for the WAN links. Set equal or varied weightage (e.g., 50–50 for load balancing). User must ensure that the sum of the weighting % for all WAN links must be 100%.
Click the Save button to create the WAN Profile.
Click the
 icon to delete the WAN Profile.
icon to delete the WAN Profile.
LAN
Select the LAN option from the side menu bar to open the LAN tab. This tab enables the user to manage VLANs and network address configurations.
-20250811-155249.png?inst-v=a84c6a6d-1a04-4602-8458-1957efbf2cd0)
LAN
The user can press on the Refresh button to refresh the page and get the latest data. By default, this screen refreshes every 30 seconds.
The table shows the following information:
Network Alias - A name assigned to identify the LAN or VLAN network.
VLAN ID - The numeric VLAN tag that separates and identifies the network in a trunked environment.
WAN Profile – The WAN routing profile associated with this LAN, determining how outbound traffic is handled.
Interface IP / Subnet - Define the IP address and subnet mask (e.g., 192.168.1.1/24).
DHCP - Indicates whether the DHCP server is enabled to automatically assign IP addresses to connected clients.
Gateway Address - The default IP gateway for devices on this network.
DNS Servers - Comma-separated DNS addresses (e.g., 8.8.8.8,1.1.1.1).
Actions -
Click the
icon to edit the Network Alias, Interface IP, Profile Name, Enable/Disable Management Network, Enable/Disable Captive Access Network, and DHCP details.
Click the
 icon to delete the LAN Network.
icon to delete the LAN Network.
Add LAN Network
Click the Add LAN Network button to add a new LAN Network with VLAN tagging and optional DHCP configuration.
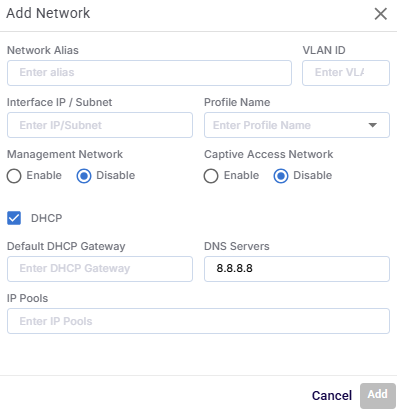
Add Network
In the Network Alias field, enter a name for the LAN or VLAN network .
In the VLAN ID field, tag used to segment network traffic. Allowed Values: 1–4094 (must be unique within the device).
Enter the Interface IP/Subnet. This assigns the IP address and subnet mask to this network interface.
Select the WAN Profile Name that determines routing and outbound connectivity for the LAN.
In the Management Network field, select the Enable radio button to mark this LAN as the management VLAN, used for device configuration access.
In the Captive Access Network field, select the Enable radio button to enable a captive portal for network authentication.
Select the DHCP checkbox to enable the DHCP server functionality for this LAN. Additional DHCP-related fields become active.
Enter the Default DHCP Gateway. This sets the gateway IP assigned to clients. Usually matches the Interface IP.
Enter the DNS Servers. This specifies the DNS resolvers provided to clients.
Enter the IP Pools. This defines the range of IP addresses the DHCP server can assign to clients.
Click the Add button to add the new LAN Network.
Fields dynamically enable/disable based on DHCP selection.
VLANs must be unique and valid; duplicate detection and validation are performed.
Only valid subnet formats are accepted.
Management and captive settings trigger icon display in the main LAN view.
Wi-Fi
Select the Wi-Fi option from the side menu bar to open the Wi-Fi tab. This tab enables the user to configure Wi-Fi SSIDs and security.
-20250811-201251.png?inst-v=a84c6a6d-1a04-4602-8458-1957efbf2cd0)
Wi-Fi
The user can press on the Refresh button to refresh the page and get the latest data. By default, this screen refreshes every 30 seconds.
The table shows the Wi-Fi Interfaces List with the following information:
SSID – The broadcast name of the wireless network that clients will see and connect to.
LAN Name – The LAN or VLAN network that the Wi-Fi interface is mapped to for routing and IP assignment.
Wi-Fi Band – The frequency band used for wireless communication (e.g., 2.4GHz for better range, 5GHz for higher speed).
Channel – The specific wireless channel in use.
Mode – The operational mode of the Wi-Fi interface, typically Access Point for providing network access to clients.
Security – The wireless encryption method used, such as WPA2/WPA3 for secured access or Open for no authentication.
Actions –
Click the
icon to edit the WiFi interface.
Click the
icon to delete the Wi-Fi interface configuration.
Add Wi-Fi Interface
Click the Add Wifi Interface button to add a new Wifi Interface, define its operational mode, assign it to a LAN, and set its security options.
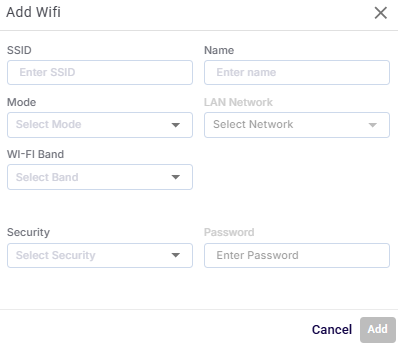
Add Wifi
In the SSID field, enter a public name of the Wi-Fi network that will be broadcast for client devices to connect to.
In the Name field, enter an alias for the Wi-Fi interface, used within the device’s configuration interface.
In the Mode field, select the operational role of the Wi-Fi interface from the dropdown menu. Typically Access Point (default) to provide connectivity.
In the LAN Network field, select a LAN network from the dropdown menu to associate the Wi-Fi interface with a specific LAN or VLAN. This determines IP addressing and routing for connected clients.
In the Wifi Band field, select the frequency range for the network.
2.4GHz – Longer range, better wall penetration, but slower speeds.
5GHz – Higher speeds, less interference, shorter range.
In the Security field, select the Security type - WPA2/WPA3 or Open.
If the Security is selected as WPA2/WPA3, set a password in the Password field. The password is key that users must enter to join the Wi-Fi network.
Open – No password required
Note: Use a strong, complex password to prevent unauthorized access.
The 'Add' button becomes active once all mandatory fields are filled.
Click the Add button to create the interface.
Click the Cancel button to discard the input and close the dialog.
SSID must be unique within the same band.
Mode and band compatibility are validated based on interface capabilities.
LAN mapping defines routing and IP assignment behavior for connected devices.
Cellular
Select the Cellular option from the side menu bar. This tab provides visibility and control over the device’s cellular modem, SIM cards, carrier details, and SIM failover behavior. It is used to monitor cellular connectivity and configure SIM priority for uninterrupted network access.
The Cellular tab is not displayed if the modem is not connected.
Cellular features are not available for users with an Essential license.
Instead, the Cellular tab displays a single informational block with the message:
“Upgrade to a Standard license or higher to access Cellular features.”Cellular functionality is supported only on Standard and higher license tiers.
Controller
The controller tab is selected by default. This section displays real-time cellular modem status, SIM details, and network information.
-20260122-070922.png?inst-v=a84c6a6d-1a04-4602-8458-1957efbf2cd0)
Controller
Active Label - This indicates the SIM currently used for cellular connectivity.
Refresh - Fetches the latest cellular and SIM status from the device.
Synced - Confirms that the SIM configuration is successfully applied to the device.
Device & Modem Information
Connection Status - Connected / Disconnected indicator shows the current cellular connectivity state. A green Connected status confirms the device is actively connected to a cellular network. The explanations for all supported states are as follows:
Not Available – Modem not on bus / resetting / failed
No SIM / Idle – No SIM present, cannot register
Searching – Searching for network
Registered – Registered and may connect
Connecting – Connecting to network
Verifying – Verifying data path
Connected – Successfully connected
Registration Denied – SIM denied by the network
Error – Modem error
Switching – SIM switching in progress
Click the Reset Modem
 icon to reset the modem.
icon to reset the modem.Click the Reload SIM
 icon to refresh the SIM details.
icon to refresh the SIM details.Device Model - Displays the cellular modem hardware model (e.g., AM102).
IMEI - The unique identifier of the cellular modem. Used for carrier registration and troubleshooting.
Firmware - Shows the currently installed modem firmware version.
Serial / DID - Unique serial number or Device Identification Number of the device.
SIM Slot Information
SIM A / SIM B Panels - Shows the physical SIM slots available on the device.
Displays the current SIM status:
Active – SIM currently in use.
No SIM Detected – No SIM inserted or recognized.
Standby - SIM is available but it is not currently in use.
ICCID - This is a unique identifier of the SIM card. It is useful for carrier validation and inventory tracking.
APN (Access Point Name) - The APN used to establish data connectivity with the carrier.
Carrier Name - Displays the mobile network operator (e.g., T-Mobile).
SIM Settings
Click the SIM Settings icon
 at the top right corner of the SIM Slot information section. This allows administrators to configure carrier-specific parameters for a selected SIM slot. These settings control cellular connectivity behavior, roaming, carrier selection, and network access restrictions.
at the top right corner of the SIM Slot information section. This allows administrators to configure carrier-specific parameters for a selected SIM slot. These settings control cellular connectivity behavior, roaming, carrier selection, and network access restrictions.
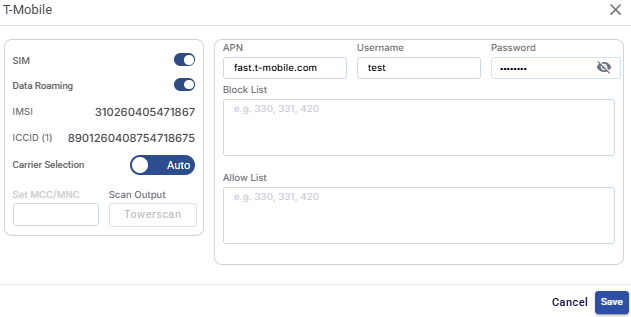
SIM Settings
SIM Toggle button - Enables or disables the selected SIM card.
Data Roaming Toggle button - Controls whether the SIM is allowed to connect to roaming networks.
Enabled SIM can connect to partner networks outside the home carrier.
Disabled SIM can connect to the home network only.
IMSI - Shows the International Mobile Subscriber Identity associated with the SIM.
ICCID - Shows the Integrated Circuit Card Identifier, a unique identifier for the SIM card.
Carrier Selection - Defines how the cellular network operator is selected.
Auto:
The modem automatically selects the best available carrier.
Recommended for most deployments.
Manual:
Allows manual selection of a specific carrier (if supported).
Manually specifies the Mobile Country Code (MCC) and Mobile Network Code (MNC).
Scan Output (Towerscan) - Scans and lists available cellular towers and networks.
Enter the APN used to connect to the carrier’s data network.
Enter the Username required for APN authentication.
Enter the Password associated with the APN username.
Enter the Block List details. This prevents the SIM from connecting to specific carrier networks. Enter comma-separated MCC/MNC values.
Enter the Allow List details. This restricts connectivity to only specified carrier networks. Enter comma-separated MCC/MNC values. If an Allow List is configured, the SIM will connect only to the listed networks.
Click Save button to apply the SIM configuration changes.
Click Cancel button to discard all changes and closes the SIM Settings screen.button to apply the SIM configuration changes.
Click Cancel button to discard all changes.
Network & Signal Information
Network Type - Shows the cellular technology in use (e.g., 5G SA).
Signal Strength - Visual indicator showing signal quality.
SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio) - Indicates signal clarity.
An SNR value above 12.5 dB indicates excellent signal quality.
An SNR value between 10 - 12.5 indicates good signal quality.
An SNR value between 7-10 indicates fair signal quality.
An SNR value below 7 indicates poor signal quality. These details are shown by the below color codes.
If Roaming is enabled on any of the SIM, it is denoted by the R icon.
-20260123-133605.png?inst-v=a84c6a6d-1a04-4602-8458-1957efbf2cd0)
Signal Strength
Band - Cellular frequency band currently used by the modem.
Bandwidth - Channel bandwidth allocated by the carrier.
MCC / MNC - Mobile Country Code / Mobile Network Code identifying the carrier network.
Cell ID - Identifier of the connected cellular tower.
PLMN - Public Land Mobile Network code of the serving network.
TX / RX Data Usage - Shows transmitted and received data volume over the cellular link.
SIM Priority
Click the SIM Priority tab. This section controls how the device selects and switches between available SIM cards.
-20260122-072602.png?inst-v=a84c6a6d-1a04-4602-8458-1957efbf2cd0)
SIM Priority
The table shows the following information:
SIM Slot - Indicates whether the SIM is in slot A or B.
Carrier - Mobile operator associated with the SIM.
IMSI - International Mobile Subscriber Identity.
ICCID - Unique SIM card identifier.
APN - Access Point Name configured for the SIM.
Carrier Selection - Indicates whether carrier selection is Auto or Manual.
Roaming - Shows whether roaming is enabled or disabled for the SIM.
SIM Priority Mode
Auto Mode (Default)
All SIMs are treated equally.
The device stays on the current SIM as long as connectivity is stable.
Automatically switches to another available SIM if signal is lost.
Manual Mode
Allows administrators to manually define SIM priority. Drag and drop on the table to set the SIM priority.
Useful when one SIM should always be preferred over others.
The device will stay on the selected SIM even if it becomes unreachable. It will not switch to another SIM automatically.
Click the Save button to apply SIM priority configuration changes.
Click the Cancel button to discard the changes.
System
Select the System option from the side menu bar to open the System tab. This tab enables the user to perform system-level actions like update software, reboot device, and configuration management.
-20250812-070825.png?inst-v=a84c6a6d-1a04-4602-8458-1957efbf2cd0)
System
The user can press on the Refresh button to refresh the page and get the latest data. By default, this screen refreshes every 30 seconds.
The Device Name field shows the name of the device in the network.
The System Uptime field shows how long the device has been running since the last reboot.
The Konnect Status field indicates whether the device is online and connected. The below color convention describes the status of the device.
Green Dot: Connected.
Red Dot: Disconnected.
The Device Model field displays the model number of the hardware.
The Latest Available Software field shows the most recent firmware/software version available for the device.
The Current Software Version field displays the software version currently installed on the device.
Click the Reboot Device button to restart the device.
Click the Update Software button to update the device to the latest available software version.
Configuration
The Software Version field shows the version of the system configuration.
The Configuration Creation Date field shows the date when the current configuration file was created.
In the File Name field, enter a name when saving the current device configuration.
Click the Save Configuration button to save the current system configuration for backup purposes.
In the Upload Device Configuration field, select the type of configuration to upload to the device from the dropdown menu. The options available are Startup, Running, Backup.
Click the Upload Configuration button to upload the selected configuration file to the device and apply it.
Association
Select the Association option from the side menu bar to open the Association tab. This tab shows the device’s current organizational association and licensing details. It also provides controls for moving the device between organizations or to warehouse or changing its license.
-20250812-073252.png?inst-v=a84c6a6d-1a04-4602-8458-1957efbf2cd0)
Association
The user can press on the Refresh button to refresh the page and get the latest data. By default, this screen refreshes every 30 seconds.
Current Device Association
Under the Current Device Association Section, the Device Hierarchical Path field shows the full organizational structure where the device is currently associated.
The format is Organization / Site / Device Name. This helps to identify the exact location of the device in large multi-site deployments.
Click the Move Device button to transfer the device to another organization or site within the management system. The Move Device dialog box opens.
Move Device Only
Select the Move Device Only (Keep Existing Site) radio button to move the device to another Organization or Site.
-20250812-074646.png?inst-v=a84c6a6d-1a04-4602-8458-1957efbf2cd0)
Move Device Only
Select the required organization from the dropdown menu in the Organization field.
Select the required site from the dropdown menu in the Site field.
The Device field shows the name of the selected device.
Select the Move Device button to move the device to the selected organization and site.
Move Site and All Devices
Select the Move Site and All Devices radio button to move an entire and all its devices to another organization.
-20250812-075518.png?inst-v=a84c6a6d-1a04-4602-8458-1957efbf2cd0)
Move Site and All Devices
Select the required organization from the dropdown menu in the Organization field.
The Site field shows the name of the selected site.
The Device field shows that all devices will be moved.
Select the Move Site button to move the site to the selected organization.
Move Device to Warehouse
Select the Move Device to Warehouse radio button to move the device back to the warehouse.
-20250812-081850.png?inst-v=a84c6a6d-1a04-4602-8458-1957efbf2cd0)
Move Device to Warehouse
The Organization field shows the name of the selected organization.
The Site field shows the name of the selected site.
The Device field shows the name of the selected Device.
Select the Move To Warehouse button to move the device to the warehouse.
License
The License field shows the type of license currently assigned to the device.
The Remaining License Term shows how much time is left before the license expires. The user can monitor this field to avoid service interruptions and plan renewals.
Click the Change License button to modify the license type or duration for the device. The Change License dialog box opens.
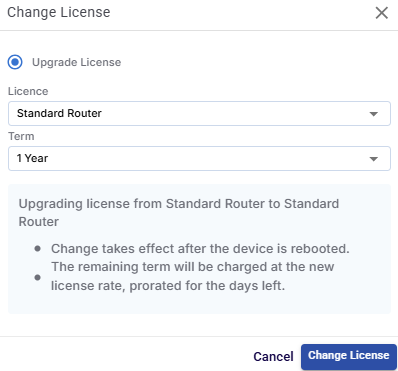
Change License
In the License field, select the required license type from the dropdown menu.
In the Term field, select the required license term from the dropdown menu.
Click the Change License button to update the license details and save the changes.
Conclusion
The Configuration dialog box centralizes all essential settings in one clean, manageable UI. Whether editing interfaces, assigning priorities, pushing system updates, or managing licenses, this screen ensures efficient administration of connected devices. Designed with scalability in mind, it empowers users to configure and control large fleets of network devices effortlessly.
