Interface Settings
The Interfaces Table shows each configured interface in EdgeOS and provides various readback data and settings to control the behavior.

Interface Settings
The following sections provides a brief description of each Field and an explanation of how to configure the available settings.
Enable / Disable
Field | Description | Configuration |
Enable / Disable | Enables or Disables the interface. Disabled Interfaces will only be shown if ‘All Interfaces’ checkbox is selected | Click/Slide to left to Disable. Click/Slide to right to Enable |
Interface Name
Field | Description | Configuration |
Interface Name with hyperlink | User can configure the static IP address of an Interface as the Static IP has advantages and the following are a few advantages.
| To configure the static IP of an Interface, perform the following steps. Steps
|
Interface Types
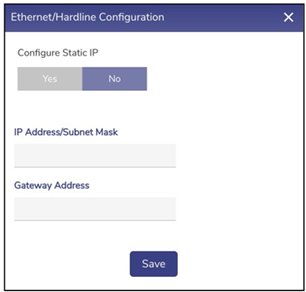
Ethernet / Hardline
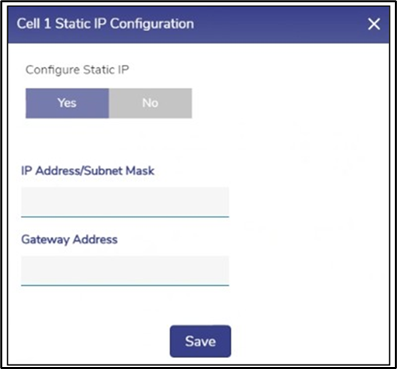
CELL Configuration
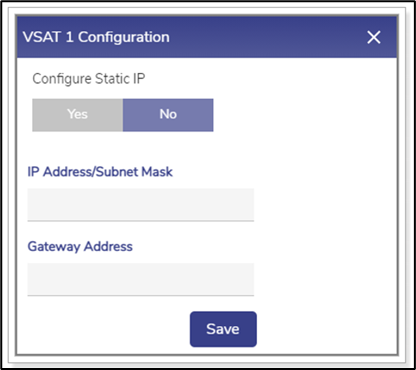
VSAT Configuration
WAN / LAN Type
Field | Description | Configuration |
WAN/LAN Type | This field shows the type of the interface. | If the Interface type is. WAN, then this field can be one of:
If Interface Type is ‘LAN’, then, this field can be one of: LAN Trunk LAN Access.
|
Alias
Field | Description | Configuration |
Alias | User can give an alias name to the entire Interface. | To configure the alias name, perform the following steps. Steps
|
Internet State
Field | Description | Configuration |
Internet State | This indicates the status of the Interface. Following are the statuses of the Interface.
| N/A |
Eth State / Reset
Field | Description | Configuration |
Eth State/Reset | This indicates the maximum capacity of the respective Ethernet cable connected to the server. | To view the Eth state details, hover on Info icon. This shows the Eth state details. State Change Count indicates the number of times the Internet State of the Interface changed since the last reboot. Refer Figure Eth State Hover. |
The info icon is blue when the Internet State is consistent for last 15 minutes and amber i when Internet State changes in last 15 minutes. (Down to UP or UP to Down). | ||
To reset Interface: Click on the reset icon This bounces the Interface if it is a physical interface. If it is a sub interface, it restarts the DHCP client. |
Eth State Details
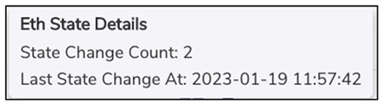
Eth State Hover
IP Address / Subnet Mask
Field | Description | Configuration |
IP Address / Subnet Mask | This indicates the address of the network, host or device address, and subnet number. | N/A |
Gateway Address
Field | Description | Configuration |
Gateway Address | This indicates that the internet modems and switches on the VLANs can be reached through the gateway address. The hardware is provided by the respective companies or vendors. The boxes connect to the network of the companies or vendors to establish internet connectivity on the site. | If WAN Type is CELL, then. To access the Cellular modem to procure details and services (data consumed by the Interface and signal strength etc.) offered by the respective company or vendor, click the IP address link. User will be routed to the URL of the company. |
To procure details and services (data consumed by the CELL (LTE) and signal strength etc.) offered by the respective company or vendor.
The user will be routed to the URL of the company. | ||
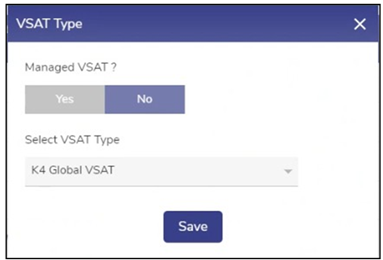
| If WAN Type is VSAT, then.
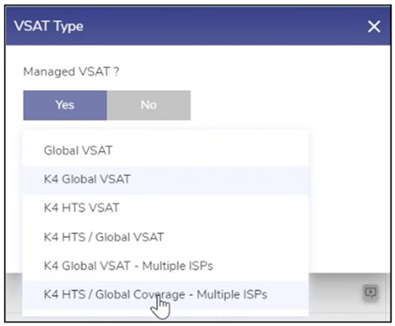
Note: By default, No is selected. This indicates that the VSAT is not provisioned by Kognitive. In the VSAT Type list, select one of the available options.
Note: SES and Hispasat are running two different iDirect platform firmware, hence the need for two modems.
Note: SES and Intelsat configurations are saved in the EdgeOS System, and appropriate configuration is loaded on the modem.
| |
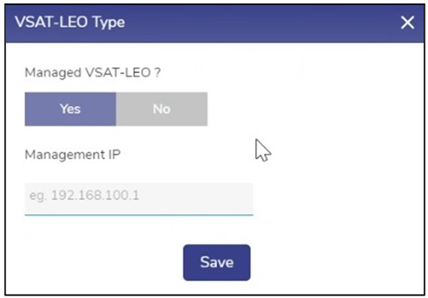
| VSAT LEO (Starlink) service and support | If WAN Type is VSAT-LEO, then
If the VSAT-LEO modem is managed by Kognitive, then click Yes. Then Management IP field is editable. By default, NO is selected. This indicates that the VSAT-LEO is not managed by Kognitive. See Figure VSAT-LEO.
Click on Yes and enter the Management IP of the VSAT LEO Management Interface. |
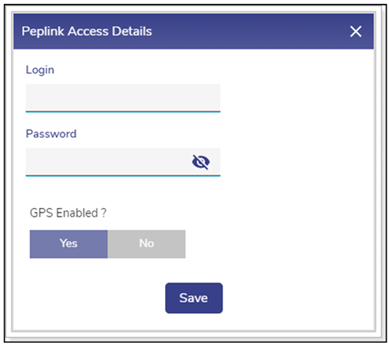
| If the WAN modem is available, then the user can add the WAN modem to Konnect Remote Access. | To add the WAN modem to the Konnect, perform the following steps. Steps
|
Gateway Details
Peplink Access Details
VSAT Type default pop-up
VSAT Type Selection
VSAT-LEO
Add to Konnect - Remote Access

Add to Konnect
Probe / Latency (ms)
Field | Description | Configuration |
Probe/Latency (msec) | Latency indicates the delay between the action and response in milliseconds. Latency is available for the Interface whose status is Up. The user can configure the probe settings for the Interface. | Each WAN type has a specific default probe setting. This is however configurable. To configure the probe settings, perform the following steps. Steps
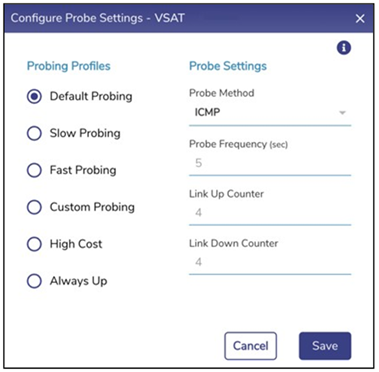
To understand the various probing profile, hover on the i icon. See Figure Probe Profiles Information. To disable the probes, select the Always Up profile of the profile. Disabling the Interface probe will expose the following threats.
Therefore, it is highly recommended not to disable the probe. However, the Interface can be disabled for high costs low priority links.
Configure the following probe settings in the Probe Settings field.
If the user selects the Default Probing, Slow Probing, and Fast Probing profile of the probe, then the probe frequency and link up and down values will become available. To define the probe frequency, the user must select the Custom Probing profile of the probe and enter the probe frequency within the range of 1 to 3600.
If the user selects the Default Probing, Slow Probing, and Fast Probing profile of the probe, then the probe frequency, link up down values will become available. Note: For VSAT FBB WAN type, the default Probe Profile is High Cost. To define the link up counter, the user must select the Custom Probing profile of the probe and enter the link up counts within range of 1 to 100.
If the user selects the Default Probing, Slow Probing, and Fast Probing profile of the probe, then the probe frequency and link up and down values will become available. To define the probe frequency, the user must select the Custom Probing profile of the probe and enter the link down counts within the range of 1 to 100.
|
| User can view the Probe/Latency chart of the Interface. | To view the Probe/Latency chart of the Interface, click Chart icon corresponding to the Interface. The Link Status section appears on the Performance Chart. |
Probe Profiles

Probe Profiles Information
Probe Settings
Configure Probe
DNS Servers
Field | Description | Configuration |
DNS Servers | This indicates the initial DNS used by the device to convert the name of the host to an IP address. However, a maximum of three DNSs’ can be configured. | N/A |
Speed Test (Speedtest)
Run an instant Speed Test, or schedule automatic Speed Tests that run in the background to generate historic performance data.
Field | Description | Configuration |
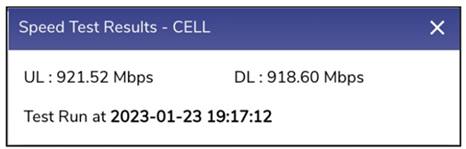
Speed Test | The user can measure the performance of a specific Interface in real-time or configure automated periodic speed test | Click Speed Test. The Speed Test Results pop-up window appears, see Figure Speed Test. The speed test result includes the upload and download speed in Mbps and time stamp i.e., date and time when the speed test was performed. The speed test can be performed for the Interface whose state is Up. |
Default Speed Test settings per WAN type are:
To configure the periodic speed test, perform the following steps. Steps
To select a different periodicity value (other than default), Click the Speed Test Periodicity list, select the desired value, see Figure Speed Test List.
|
Edit Speed Test Settings
Periodic Speed Test (Speedtest)
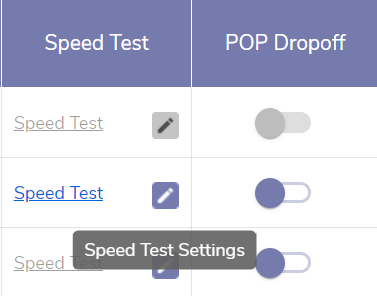
Click the Pencil Icon next to Speed Test to configure periodic speed tests for an individual WAN source. The data from these periodic tests can be viewed in Performance Charts > Speed Test Results.
Periodic Speed Tests use an amount of data proportional to the throughput/speed of the WAN source. WAN sources with high throughput (Download and Upload Mbps) will potentially use a large amount of data. Take care in selecting the period/frequency of speedtests for metered links.
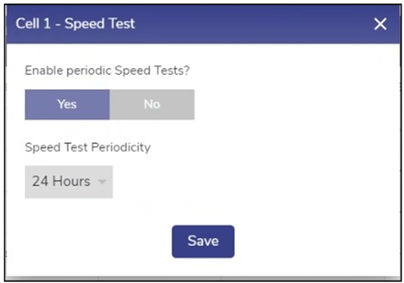
Speed Test
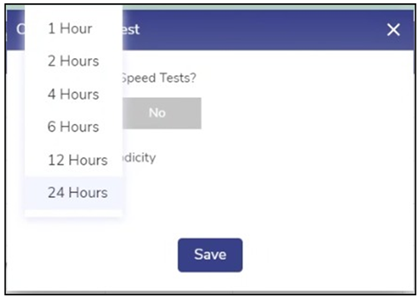
Speed Test List
Speed Test
Public IP Address (Display)
Fields | Description | Configuration |
Public IP Address/Service Provider | Public IP Address the public or global IP address used to access the internet. The public or global IP address is assigned by the internet service provider (ISP). Service Provider indicates the name of ISP. | This information is available once speed test is run successfully on this interface, either manually or periodically. |
POP Dropoff
Point Of Presence
Fields | Description | Configuration |
POP Dropoff (US Internet) | Drop off traffic at the designated POP dropoff | Use the toggle to turn ON-OFF the POP dropoff feature |
